import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
sns.set_context("talk")
%matplotlib inline
import plotly.offline as py
py.init_notebook_mode(connected=False)
import plotly.graph_objs as go
import plotly.figure_factory as ff
import cufflinks as cf
cf.set_config_file(offline=False, world_readable=True, theme='ggplot')
Feature Engineering¶
In this notebook we will explore a key part of data science, feature engineering: the process of transforming the representation of model inputs to enable better model approximation. Feature engineering enables you to:
- encode non-numeric features to be used as inputs to common numeric models
- capture domain knowledge (e.g., the perceived loudness or sound is the log of the intensity)
- transform complex relationships into simple linear relationships
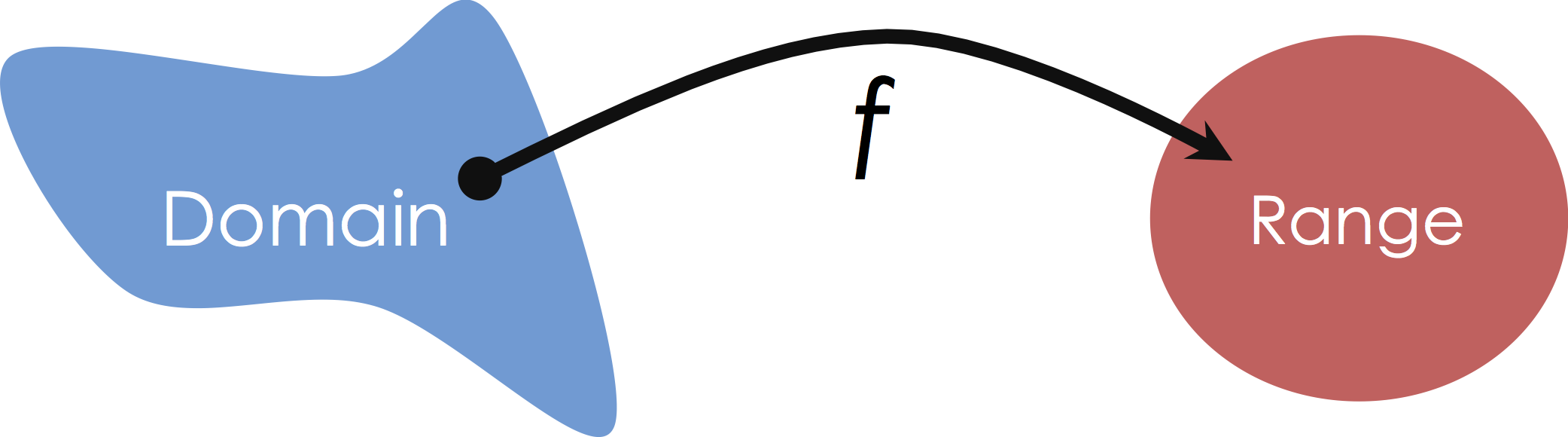
Mapping from Domain to Range¶
In the supervised learning setting were are given $(X,Y)$ pairs with the goal of learning the mapping from $X$ to $Y$. For example, given pairs of square footage and price we want to learn a function that captures (or at least approximates) the relationship between square feet and price. Our functional approximation is some form of typically parametric mapping from some domain to some range:
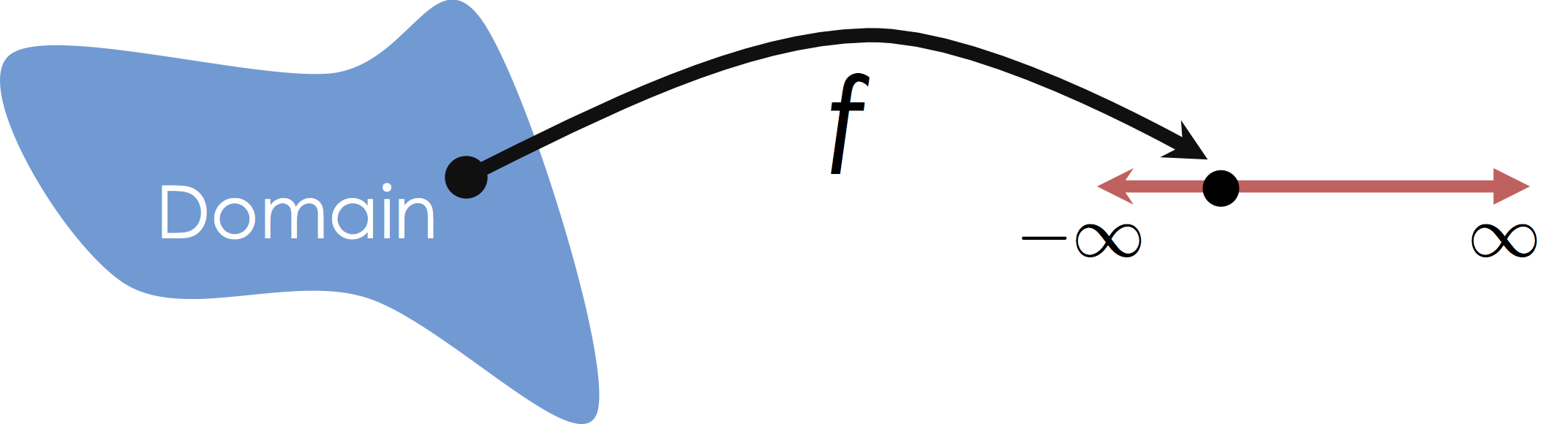
In this class we will focus on Multiple Regression in which we consider mappings from potentially high-dimensional input spaces onto the real line (i.e., $y \in \mathbb{R}$):
It is worth noting that this is distinct from Multivariate Regression in which we are predicting multiple (confusing?) response values (e.g., $y \in \mathbb{R}^q$).
Not all Domains are Quantitative¶
Suppose we are given the following table:
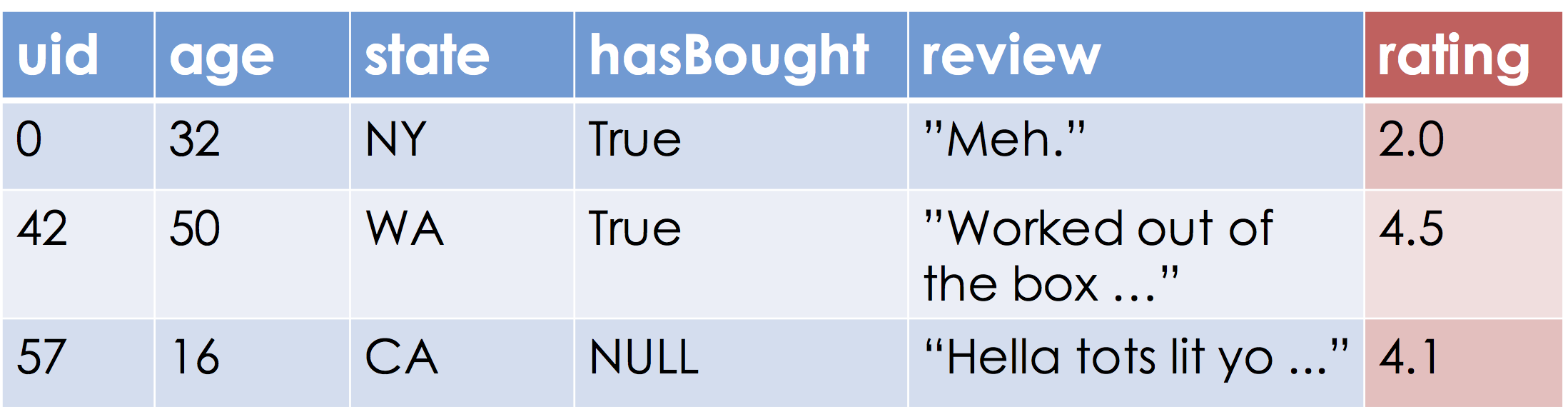
Our goal is to learn a function that approximates the relationship between the blue and red columns. Let's assume the range, "Ratings", are the real numbers (this may be a problem if ratings are between [0, 5] but more on that later).
What is the domain of this function?
The schema of the relational model provides one possible answer:
RatingsData(uid INTEGER, age FLOAT,
state VARCHAR, hasBought BOOLEAN,
review VARCHAR, rating FLOAT)
Which would suggest that the domain is then:
integers, real numbers, strings, booleans, and more strings.
Unfortunately, the techniques we have discussed so far and most of the techniques in machine learning and statistics operate on real-valued vector inputs $x \in \mathbb{R}^d$ (or for the statisticians $x \in \mathbb{R}^p$).
Goal:¶
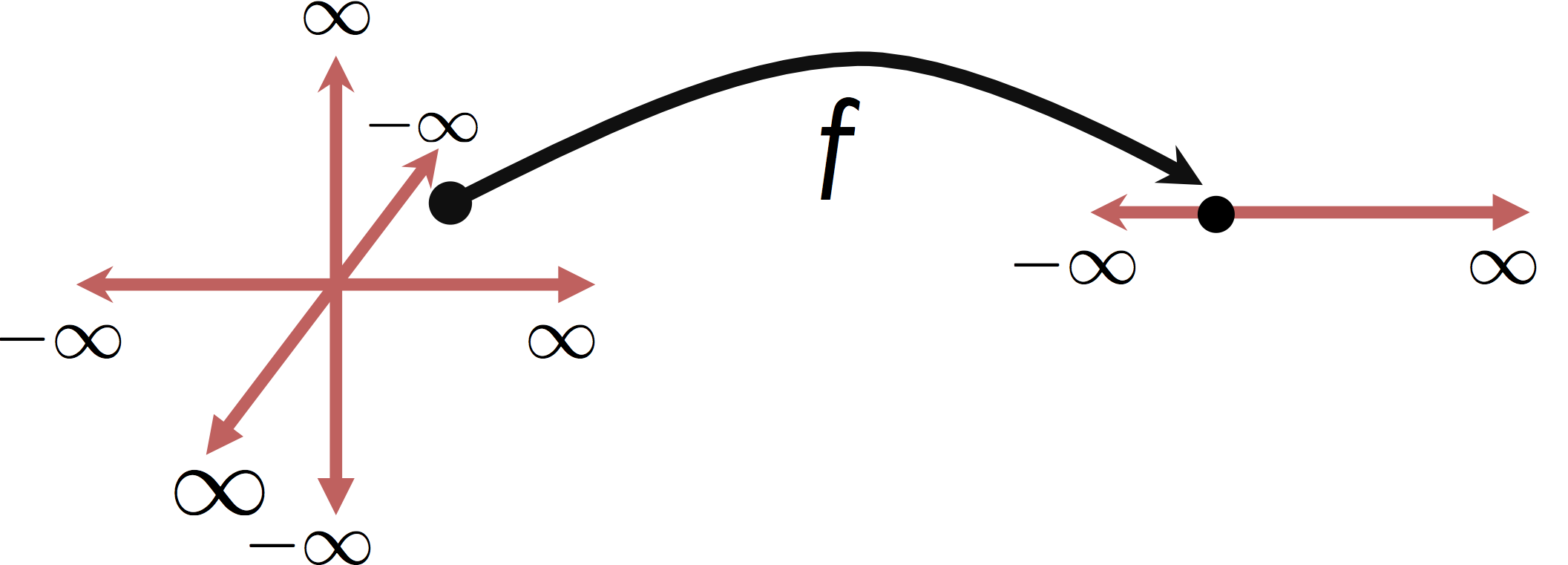
Moreover, many of these techniques, especially the linear models we have been studying, assume the inputs are qauntitative variables in which the relative magnitude of the feature encode information about the response variable.
In the following we define several basic transformations to encode features as real numbers.
Basic Feature Engineering: Get $\mathbb{R}$¶
Our first step as feature engineers is to translate our data into a form that encodes each feature as a continuous variable.
The Uninformative Feature: uid¶
The uid was likely used to join the user information (e.g., age, and state) with some Reviews table. The uid presents several questions:
- What is the meaning of the
uidnumber? - Does the magnitude of the
uidreveal information about the rating?
There are several answers:
Although numbers, identifiers are typically categorical (like strings) and as a consequence the magnitude has little meaning. In these settings we would either drop or one-hot encode the
uid. We will return to feature dropping and one-hot-encoding in a moment.There are scenarios where the magnitude of the numerical
uidvalue contains important information. When user ids are created in consecutive order, larger user ids would imply more recent users. In these cases we might to interpret theuidfeature as a real number and keep it in our model.
Dropping Features¶
While uncommon there are certain scenarios where manually dropping features might be helpful:
when the features does not to contain information associated with the prediction task. Dropping uninformative features can help to address over-fitting, an issue we will discuss in great detail soon.
when the feature is not available at prediction time. For example, the feature might contain information collected after the user entered a rating. This is a common scenario in time-series analysis.
However, in the absence of substantial domain knowledge, we would prefer to use algorithmic techniques to help eliminate features. We will discuss this in more detail when we return to regularization.
The Continuous age Feature¶
The age feature encodes the users age. This is already a continuous real number so no additional feature transformations are required. However, as we will soon see, we may introduce additional related features (e.g., indicators for various age groups or non-linear transformations).
The Categorical state Feature¶
The state feature is a string encoding the category (one of the 50 states). How do we meaningfully encode such a feature as one or more real-numbers?
We could enumerate the states in alphabetical order AL=0, AK=2, ... WY=49. This is a form of dictionary encoding which maps each category to an integer. However, this would likely be a poor feature encoding since the magnitude provides little information about the rating.
Alternatively, we might enumerate the states based on their geographic region (e.g., lower numbers for coastal states.). While this alternative dictionary encoding may provide information there is better way to encode categorical features for machine learning algorithms.
One-Hot Encoding¶
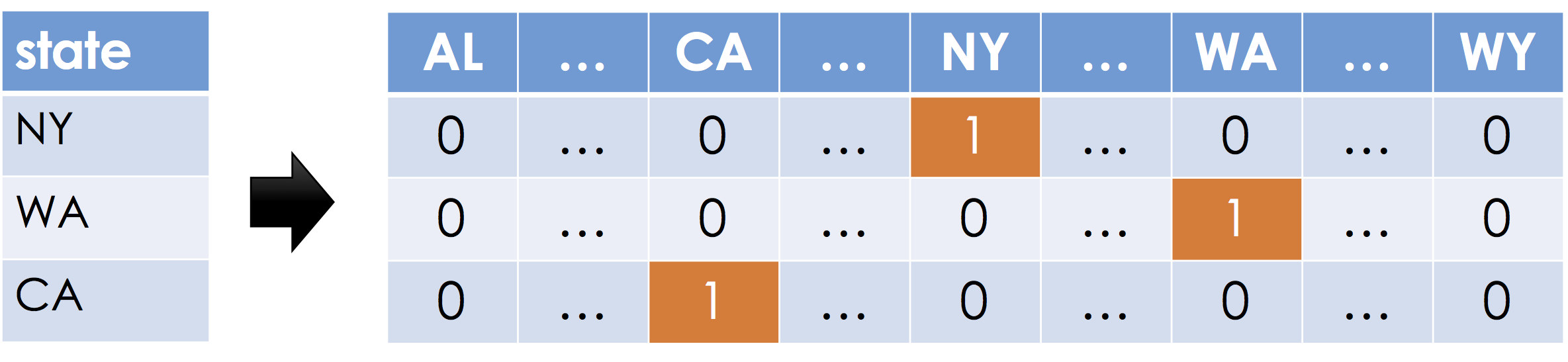
One-Hot encoding, sometimes also called dummy encoding is a simple mechanism to encode categorical data as real numbers such that the magnitude of each dimension is meaningful. Suppose a feature can take on $k$ distinct values (e.g., $k=50$ for 50 states in the United Stated). For each distinct possible value a new feature (dimension) is created. For each record, all the new features are set to zero except the one corresponding to the value in the original feature.
The term one-hot encoding comes from a digital circuit encoding of a categorical state as particular "hot" wire:
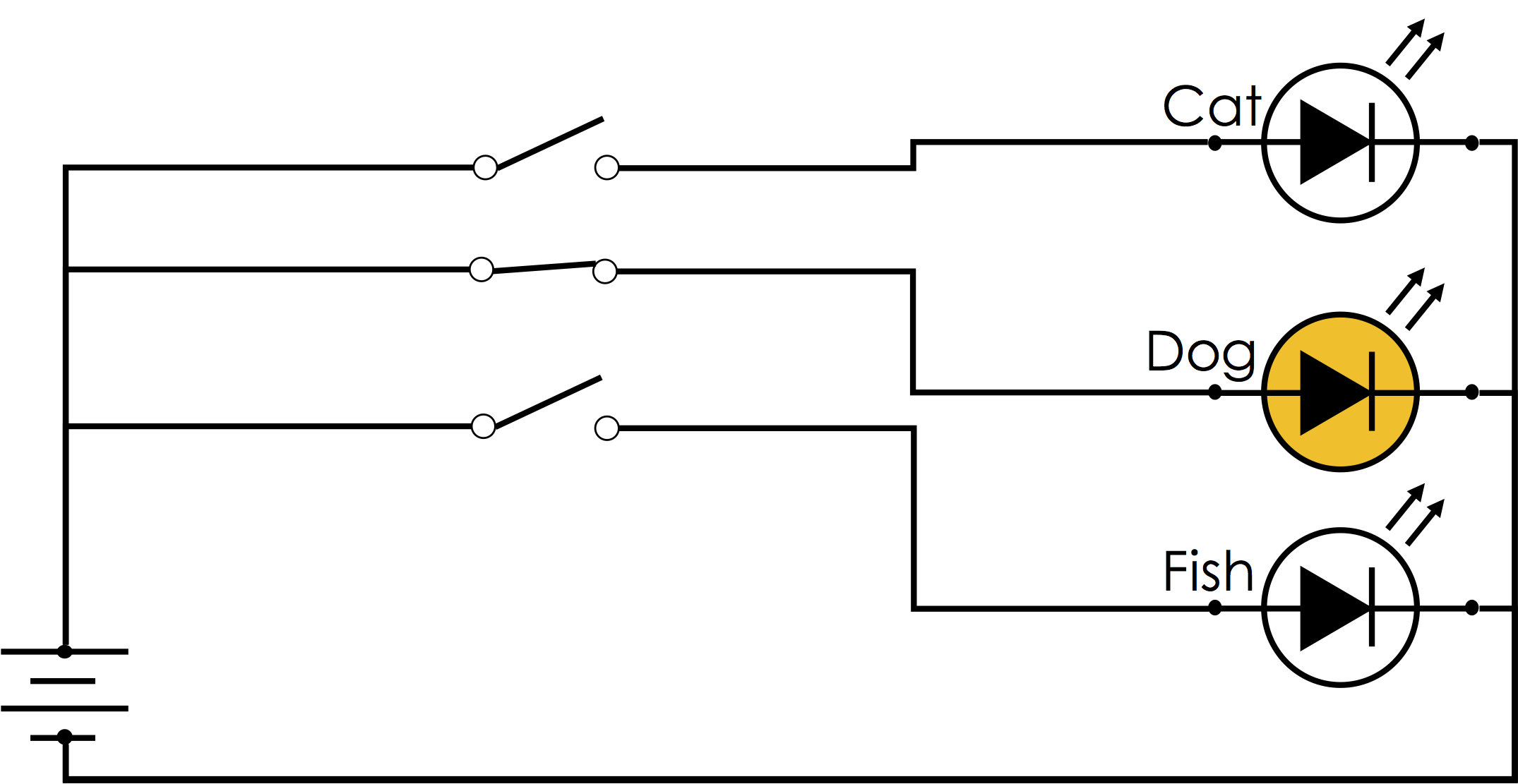
One-Hot Encoding in Pandas¶
Here we create a toy DataFrame of pets including their name and kind:
df = pd.DataFrame({
"name": ["Goldy", "Scooby", "Brian", "Francine", "Goldy"],
"kind": ["Fish", "Dog", "Dog", "Cat", "Dog"],
"age": [0.5, 7., 3., 10., 1.]
}, columns = ["name", "kind", "age"])
Pandas has a built in function to construct one-hot encodings called get_dummies
pd.get_dummies(df['kind'])
pd.get_dummies(df)
A serious issue with using Pandas to construct a one-hot-encoding is that we have no easy way to apply an old one-hot encoding to new data. For example, we can't somehow apply the same encoding from above for df2 below.
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
"name": ["Goldy", "Fluffy", "Goldy"],
"kind": ["Cat", "Bird", "Chihuahua"],
"age": [35, None, None]
}, columns = ["name", "kind", "age"])
df2
One-Hot Encoding in Scikit-Learn¶
Scikit-Learn also has several library for constructing one-hot-encodings that rely on a DataFrame method called to_dict.
df.to_dict(orient='records')
from sklearn.feature_extraction import DictVectorizer
vec_enc = DictVectorizer()
vec_enc.fit(df.to_dict(orient='records'))
vec_enc.transform(df.to_dict(orient='records')).toarray()
vec_enc.get_feature_names()
Applying to new data¶
One advantage of the DictVectorizer in sklearn is that we can easily apply it to new data:
vec_enc.transform(df2.to_dict(orient='records')).toarray()
The Text review Feature¶
Encoding text as a real-valued feature is especially challenging and many of the standard transformations are lossy. Moreover, all of the earlier transformations (e.g., one-hot encoding and Boolean representations) preserve the information in the feature. In contrast, most of the techniques for encoding text destroy information about the word order and in many cases key parts of the grammar.
Here we will discuss two widely used representations of text:
- Bag-of-Words Encoding: encodes text by the frequency of each word
- N-Gram Encoding: encodes text by the frequency of sequences of words of length $N$
Both of these encoding strategies are related to the one-hot encoding with dummy features created for every word or sequence of words and with multiple dummy features having counts greater than zero.
The Bag-of-Words Encoding¶
The bag-of-words encoding is widely used and a standard representation for text in many of the popular text clustering algorithms. The following is a simple illustration of the bag-of-words encoding:
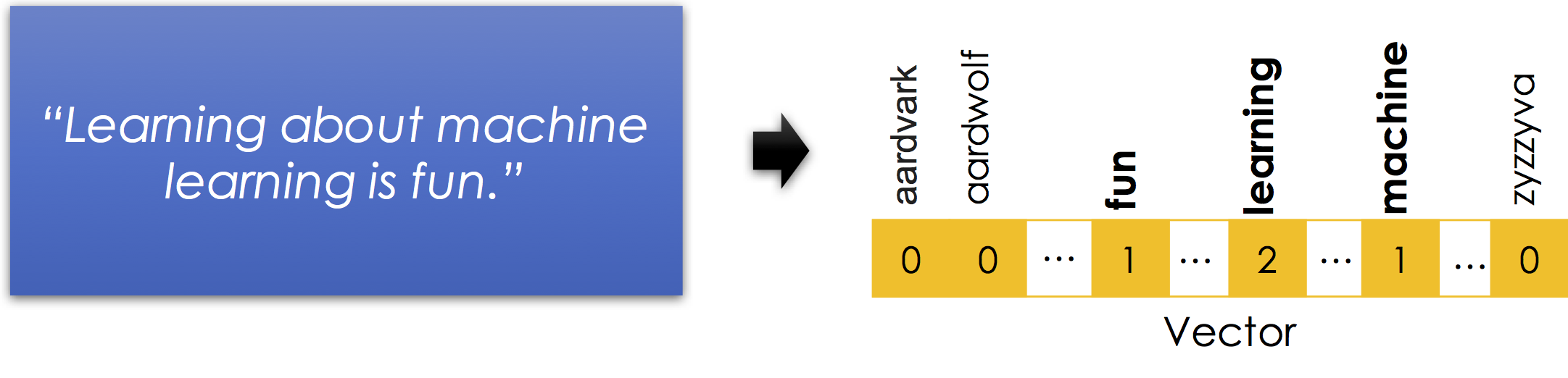
Notice
- Stop words are removed. Stop-words are words like
isandaboutthat in isolation contain very little information about the meaning of the sentence. Here is a good list of stop-words in many languages. - Word order information is lost. Nonetheless the vector still suggests that the sentence is about
fun,machines, andlearning. Thought there are many possible meanings learning machines have fun learning or learning about machines is fun learning ... - Capitalization and punctuation are typically removed.
- Sparse Encoding: is necessary to represent the bag-of-words efficiently. There are millions of possible words (including terminology, names, and misspellings) and so instantiating a
0for every word that is not in each record would be incredibly inefficient.
Why is it called a bag-of-words? A bag is another term for a multiset: an unordered collection which may contain multiple instances of each element.
Implementing the Bag-of-words Model¶
We can use sklearn to construct a bag-of-words representation of text
frost_text = [x for x in """
Some say the world will end in fire,
Some say in ice.
From what Ive tasted of desire
I hold with those who favor fire.
""".split("\n") if len(x) > 0]
frost_text
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
# Construct the tokenizer with English stop words
bow = CountVectorizer(stop_words="english")
# fit the model to the passage
bow.fit(frost_text)
# Print the words that are kept
print("Words:", list(enumerate(bow.get_feature_names())))
print("Sentence Encoding: \n")
# Print the encoding of each line
for (s, r) in zip(frost_text, bow.transform(frost_text)):
print(s)
print(r)
print("------------------")
The N-Gram Encoding¶
The N-Gram encoding is a generalization of the bag-of-words encoding designed to capture limited ordering information. Consider the following passage of text:
The book was not well written but I did enjoy it.
If we re-arrange the words we can also write:
The book was well written but I did not enjoy it.
Moreover, local word order can be important when making decisions about text. The n-gram encoding captures local word order by defining counts over sliding windows. In the following example a bi-gram ($n=2$) encoding is constructed:
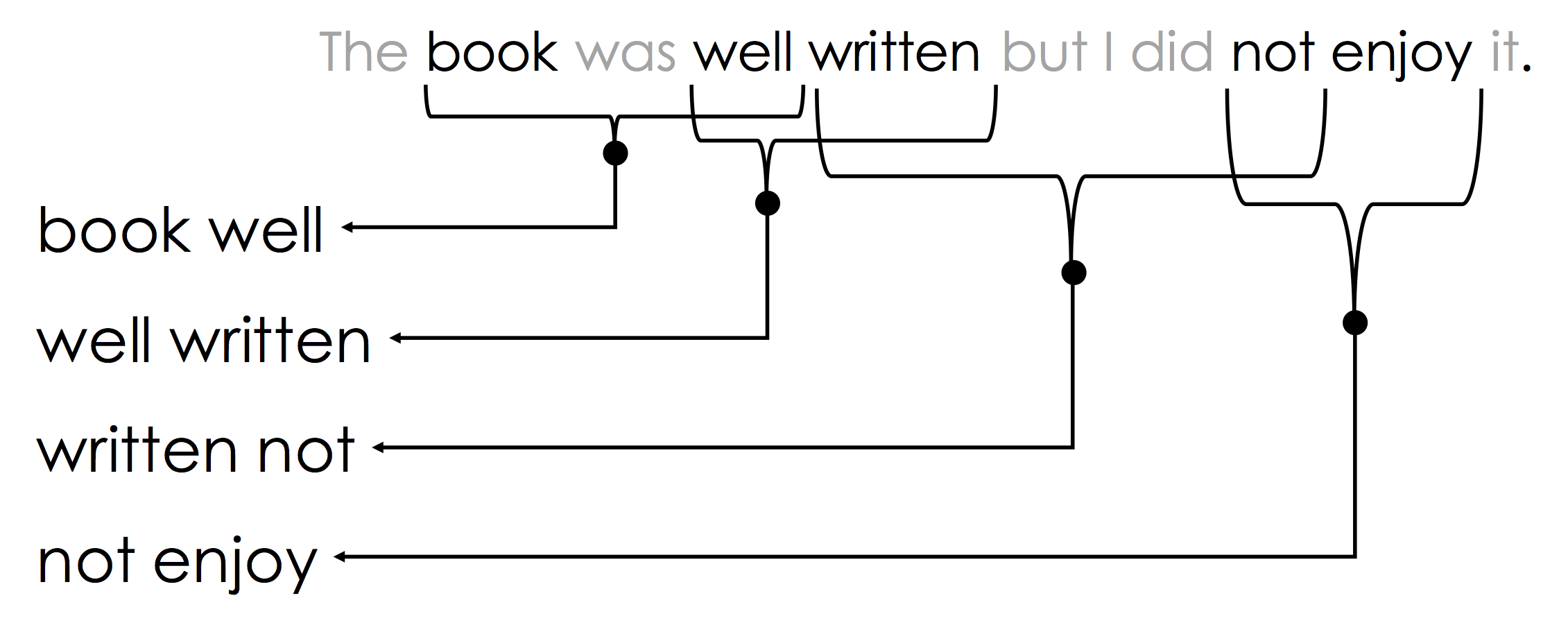
The above n-gram would be encoded in the sparse vector:
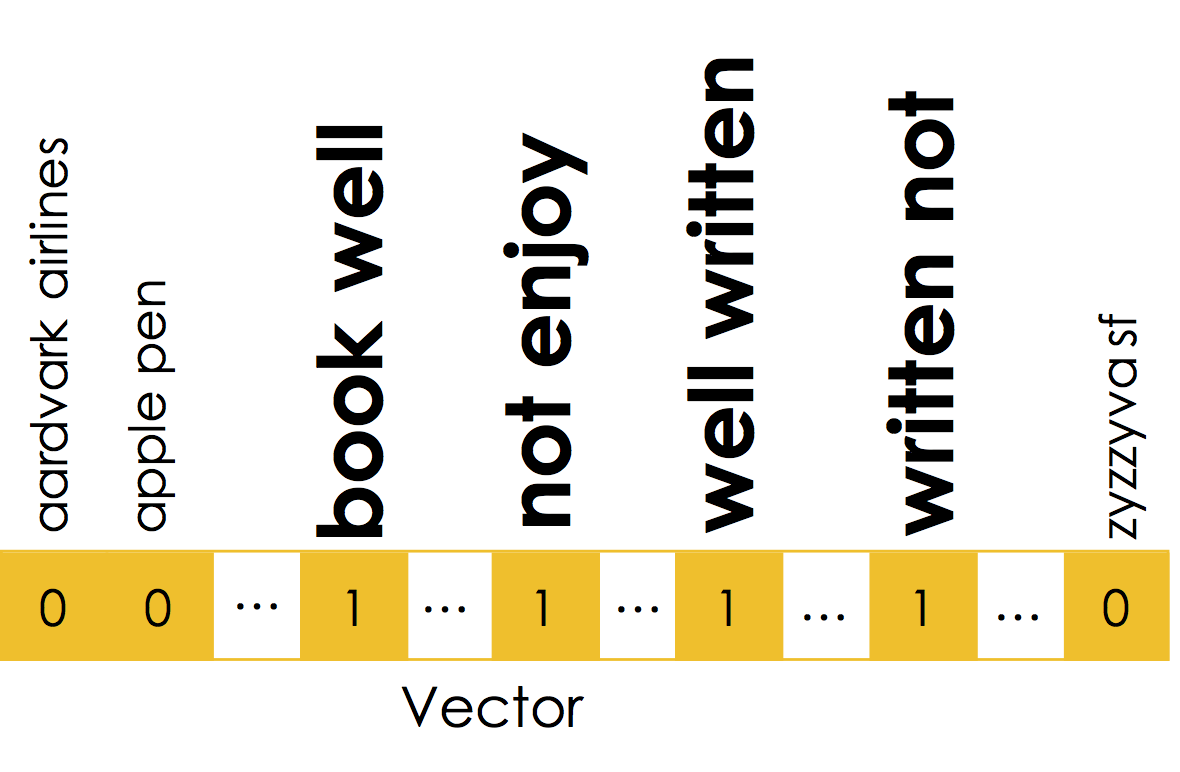
Notice that the n-gram captures key pieces of sentiment information: "well written" and "not enjoy".
N-grams are often used for other types of sequence data beyond text. For example, n-grams can be used to encode genomic data, protein sequences, and click logs.
N-Gram Issues
- The n-gram representation is hyper sparse and maintaining the dictionary of possible n-grams can be very costly. The hashing trick is a popular solution to approximate the sparse n-gram encoding. In the hashing trick each n-gram is mapped to a relatively large (e.g., 32bit) hash-id and the counts are associated with the hash index without saving the n-gram text in a dictionary. As a consequence, multiple n-grams are treated as the same.
- As $N$ increase the chance of seeing the same n-grams at prediction time decreases rapidly.
# Construct the tokenizer with English stop words
bigram = CountVectorizer(ngram_range=(1, 2))
# fit the model to the passage
bigram.fit(frost_text)
# Print the words that are kept
print("\nWords:",
list(zip(range(0,len(bigram.get_feature_names())), bigram.get_feature_names())))
print("\nSentence Encoding: \n")
# Print the encoding of each line
for (s, r) in zip(frost_text, bigram.transform(frost_text)):
print(s)
print(r)
print("------------------")
Calculating Optimal Theta¶
We'll give an example here of how to compute the optimal Theta for linear models. For conceptual simplicity, we will use data with only one dimension, and our feature functions will be extremely simple.
train_data = pd.read_csv("data/toy_training_data.csv")
train_data.head()
# Visualize the data ---------------------
train_points = go.Scatter(name = "Training Data",
x = train_data['X'], y = train_data['Y'],
mode = 'markers')
# layout = go.Layout(autosize=False, width=800, height=600)
py.iplot(go.Figure(data=[train_points]))
Solving the Normal Equations¶
Extracting the Data as Matrices¶
# Note that we select a list of columns to return a matrix (n,p)
X = train_data[['X']].values
print("X shape:", X.shape)
Y = train_data['Y'].values
print("Y shape:", Y.shape)
Adding a Bias Column¶
Below, we add a second column to our feature matrix, all equal to 1. This corresponds to a fixed bias that is applied to all data pints. Equivalently, you can think of our feature functions as:
$$\phi_1(x) = x$$ $$\phi_2(x) = 1$$
Phi = np.hstack([X, np.ones((len(X), 1))])
Phi[1:5,:]
Solving for $\hat{\theta{}}$¶
There are multiple ways to solve for $\hat{\theta{}}$. Following the solution to the normal equations:
$$\large \hat{\theta{}} = \left(\Phi^T \Phi\right)^{-1} \Phi^T Y $$
we get:
theta_hat = np.linalg.inv(Phi.T @ Phi) @ Phi.T @ Y
theta_hat
However computing inverting and multiplying (i.e., solving) can be accomplished with a special routine more efficiently:
$$\large A^{-1}b = \texttt{solve}(A, b) $$
theta_hat = np.linalg.solve(Phi.T @ Phi, Phi.T @ Y)
theta_hat
Given our theta, we can now compute predictions for each X.
y_hat = Phi @ theta_hat
y_hat
And manually comparing these to our original data:
Y
It's hard to see how well we did, so let's turn to visualization.
Visualizing the fit¶
To visualize the fit line we will make a set of predictions at 10 evenly spaced points.
X_query = np.linspace(train_data['X'].min()-1, train_data['X'].max() +1, 1000)
Phi_query = np.hstack([X_query[:,np.newaxis], np.ones((len(X_query),1))])
y_query_pred = Phi_query @ theta_hat
We can then plot the residuals along with the line.
# Define the least squares regression line
basic_line = go.Scatter(name = r"Linear Model", x=X_query, y = y_query_pred)
# Definethe residual lines segments, a separate line for each
# training point
residual_lines = [
go.Scatter(x=[x,x], y=[y,yhat],
mode='lines', showlegend=False,
line=dict(color='black', width = 0.5))
for (x, y, yhat) in zip(train_data['X'], train_data['Y'], y_hat)
]
# Combine the plot elements
py.iplot([train_points, basic_line] + residual_lines)
Examining the Residuals¶
It is often helpful to examine the residuals. Ideally the residuals should be normally distributed.
residuals = train_data['Y'] - y_hat
sns.distplot(residuals)
# plt.savefig("residuals.pdf")
We might also plot $\hat{Y}$ vs $Y$. Ideally, the data should be along the diagonal.
# Plot.ly plotting code
py.iplot(go.Figure(
data = [go.Scatter(x=train_data['Y'], y=y_hat, mode='markers', name="Points"),
go.Scatter(x=[-10, 50], y = [-10, 50], line=dict(color='black'),
name="Diagonal", mode='lines')],
layout = dict(title=r"Y_hat vs Y Plot", xaxis=dict(title="Y"),
yaxis=dict(title=r"$\hat{Y}$"))
))
The sum of the residuals should be?
np.sum(residuals)
Using a Package to estimate the linear model¶
In practice, it is generally better to use specialized software packages for linear regression. In Python, scikit-learn is the standard package for regression.

Here we will take a very brief tour of how to use scikit-learn for regression. Over the next few weeks we will use scikit-learn for a range of different task.
You can use the the scikit-learn linear_model package to compute the normal equations. This package supports a wide range of generalized linear models. For those who are interested in studying machine learning, I would encourage you to skim through the descriptions of the various models in the linear_model package. These are the foundation of most practical applications of supervised machine learning.
from sklearn import linear_model
Intercept Term Scikit-learn can automatically add the intercept term. This can be helpful since you don't need to remember to add it later when making a prediction. In the following we create a model object.
line_reg = linear_model.LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True)
We can then fit the model in one line (this solves the normal equations.
# Fit the model to the data
line_reg.fit(train_data[['X']], train_data['Y'])
np.hstack([line_reg.coef_, line_reg.intercept_])
y_hat_sklearn = line_reg.predict(train_data[['X']])
y_hat_sklearn
These are, of course, almost the same as our values predicted just using the normal equation.
y_hat
Using Feature Functions to Improve Our MOdel¶
Plotting against dimensions in X¶
When plotted against any one dimension we don't want to see any patterns:
# Plot.ly plotting code
py.iplot(go.Figure(
data = [go.Scatter(x=train_data['X'], y=residuals, mode='markers')],
layout = dict(title="Residual Plot", xaxis=dict(title="X"),
yaxis=dict(title="Residual"))
))
Transforming the Toy Data¶
In our toy data set we observed a cyclic pattern. Here we construct a $\phi$ to capture the cyclic nature of our data and visualize the corresponding hyperplane.
In the following cell we define a function $\phi$ that maps $x\in \mathbb{R}$ to the vector $[x,\sin(x)] \in \mathbb{R}^2$
$$ \large \phi(x) = [x, \sin(x)] $$
Why not:
$$ \large \phi(x) = [x, \sin(\theta_3 x + \theta_4)] $$
This would no longer be linear $\theta$. However, in practice we might want to consider a range of $\sin$ basis:
$$ \large \phi_{\alpha,\beta}(x) = \sin(\alpha x + \beta) $$
for different values of $\alpha$ and $\beta$. The parameters $\alpha$ and $\beta$ are typically called hyperparameters because (at least in this setting) they are not set automatically through learning.
def sin_phi(x):
return np.hstack([x, np.sin(x)])
Phi = sin_phi(train_data[["X"]])
Phi[:5]
Fit a Linear Model on $\Phi$¶
We can again use the scikit-learn package to fit a linear model on the transformed space.
Fitting the Basic Linear Model¶
from sklearn import linear_model
basic_reg = linear_model.LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True)
basic_reg.fit(train_data[['X']], train_data['Y'])
Fitting the Transformed Linear Model on $\Phi$¶
from sklearn import linear_model
sin_reg = linear_model.LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True)
sin_reg.fit(sin_phi(train_data[["X"]]), train_data['Y'])
Making Predictions at Query Locations¶
X_query = np.linspace(train_data['X'].min()-1, train_data['X'].max() +1, 100)
Y_basic_query = basic_reg.predict(X_query[:, np.newaxis])
Y_sin_query = sin_reg.predict(sin_phi(X_query[:, np.newaxis]))
Visualizing the Fit¶
# Define the least squares regression line
basic_line = go.Scatter(name = r"Basic Model", x=X_query, y = Y_basic_query)
sin_line = go.Scatter(name = r"Transformed Model", x=X_query, y = Y_sin_query)
# Definethe residual lines segments, a separate line for each
# training point
residual_lines = [
go.Scatter(x=[x,x], y=[y,yhat],
mode='lines', showlegend=False,
line=dict(color='black', width = 0.5))
for (x, y, yhat) in zip(train_data['X'], train_data['Y'],
sin_reg.predict(sin_phi(train_data[["X"]])))
]
# Combine the plot elements
py.iplot([train_points, basic_line, sin_line] + residual_lines)
Linear Model in a Transformed Space¶
As discussed earlier the model we just constructed, while non-linear in $x$ is actually a linear model in $\phi(x)$ and we can visualize that linear model's structure in higher dimensions.
# Plot the data in higher dimensions
phi3d = go.Scatter3d(name = "Raw Data",
x = Phi[:,0], y = Phi[:,1], z = train_data['Y'],
mode = 'markers',
marker = dict(size=3),
showlegend=False
)
# Compute the predictin plane
(u,v) = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-10,10,5), np.linspace(-1,1,5))
coords = np.vstack((u.flatten(),v.flatten())).T
ycoords = sin_reg.predict(coords)
fit_plane = go.Surface(name = "Fitting Hyperplane",
x = np.reshape(coords[:,0], (5,5)),
y = np.reshape(coords[:,1], (5,5)),
z = np.reshape(ycoords, (5,5)),
opacity = 0.8, cauto = False, showscale = False,
colorscale = [[0, 'rgb(255,0,0)'], [1, 'rgb(255,0,0)']]
)
# Construct residual lines
Yhat = sin_reg.predict(Phi)
residual_lines = [
go.Scatter3d(x=[x[0],x[0]], y=[x[1],x[1]], z=[y, yhat],
mode='lines', showlegend=False,
line=dict(color='black'))
for (x, y, yhat) in zip(Phi, train_data['Y'], Yhat)
]
# Label the axis and orient the camera
layout = go.Layout(
scene=go.Scene(
xaxis=go.XAxis(title='X'),
yaxis=go.YAxis(title='sin(X)'),
zaxis=go.ZAxis(title='Y'),
aspectratio=dict(x=1.,y=1., z=1.),
camera=dict(eye=dict(x=-1, y=-1, z=0))
)
)
py.iplot(go.Figure(data=[phi3d, fit_plane] + residual_lines, layout=layout))
Error Estimates¶
How well are we fitting the data? We can compute the root mean squared error.
def rmse(y, yhat):
return np.sqrt(np.mean((yhat-y)**2))
basic_rmse = rmse(train_data['Y'], basic_reg.predict(train_data[['X']]))
sin_rmse = rmse(train_data['Y'], sin_reg.predict(sin_phi(train_data[['X']])))
py.iplot(go.Figure(data =[go.Bar(
x=[r'Basic Regression',
r'Sine Transformation'],
y=[basic_rmse, sin_rmse]
)], layout = go.Layout(title="Loss Comparison",
yaxis=dict(title="RMSE"))))